-
Session 1: Revision of Python
-
Session 2: List in Python
-
-
Session 3: Numpy Part-1
-
Session 4: Numpy Part-2
-
Session 5: Matplotlib Part-1
-
Session 6: Matplotlib Part-2
-
-
Session 7: Microbit-AI Exercise Timer Part-1
-
-
Session 8: Microbit-AI Exercise Timer Part-2
-
Session 9: Introduction to Pandas: Python
-
Session- 10_CSV File Handling with Python
-
Session 11 & 12: Computer Vision: Introduction to Opencv
-
Session 13: Computer Vision: Introduction to Coral Bleaching
-
Session 15: Early Detection of Coral Bleaching Part-2
-
Session 16 & 17: Computer Vision: Palmer Penguins Species
-
Session 18: Palmer Penguins Species_Part-2
-
Section 19: Introduction to NLP
Session-9_Pandas.pptx
Introduction to Pandas
"Python is an experiment in how much freedom programmers need. Too much freedom and nobody can read another's code; too little and expressiveness is endangered."
--Guido Van Rossum
The quote is more relevant today than ever. As Python continues to power industries—from education to space tech—its design philosophy ensures that code remains a tool for both creativity and collaboration.
Pre-requisite Knowledge
To understand and effectively learn the content of this chapter on Pandas, students should be familiar with the following foundational concepts:
- Basic Python Programming Concepts
- Python List and Dictionary
- Loops and Iteration
- Basic File Handling
- Python IDE Usage:
- Knowledge of working in any Python platform such as:
- IDLE
- Jupyter Notebook
- PictoBlox
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, students will be able to:
- Understand the Purpose and Importance of Pandas.
- Install and Import the Pandas Library
- Recognize and Work with Pandas Data Structures
- Create and Manipulate DataFrames
- Perform Basic Data Operations
Requirements
- For Pandas library in python, we have various platforms to execute our programs.
Like: - Pictoblox, Python-IDLE, Jupyter Notebook
- In this we are going to use Python-IDLE.
👨🏫Introduction to Pandas
Pandas is a library for the Python programming language, providing fast, flexible, and expressive data structures designed to make working with structured data easy and intuitive.
The Pandas library has two primary data structures:
1. Series: A one-dimensional labelled array capable of holding data of any type.
2. DataFrame: A two-dimensional table-like structure with rows and columns, suitable for storing and manipulating tabular data.
Features of Pandas Library:
Features | Description | |
Two-Dimensional |
| |
Labeled Axes |
| |
Mixed Data Types |
| |
Flexible Indexing |
| |
Power Function |
|
Installation:
Step 1: Open Terminal or Command Prompt:
- Press Enter.
- Mac/Linux: Open the Terminal from your Application or search bar.
Step 2: Install Pandas using pip:
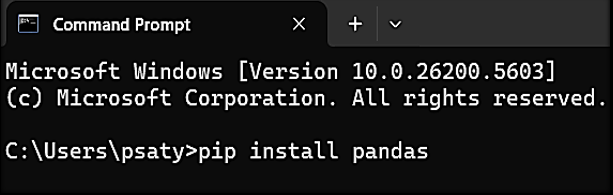
Step 3: Wait for the installation to complete.
Creating a DataFrame
A DataFrame is a two-dimensional table-like structure. You can create one from a dictionary, CSV file, or other data sources.
Creating a DataFrame in Python using the Pandas library through Python IDLE involves a few simple steps:
Step 1: Open Python IDLE.
- Go to Start Menu → Search for IDLE (Python GUI) and open it.
Step 2: Import the Pandas Library.
- pd is a commonly used alias for the Pandas library.
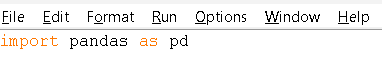
Step 3: Create a Dictionary with Data.
- This converts the dictionary into a Pandas DataFrame structure.
Step 5: Display the DataFrame
- This will show the tabular data in the output.

Final Code:

Output:
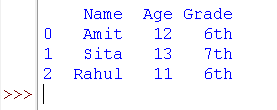
🔍 Explanation of the Output:
- Rows are automatically numbered using an index starting from 0.
- Columns are labeled (Name, Age, Grade).
- Each row represents a data record (e.g., one student's information).
- Each column represents a feature of the data (e.g., age or grade).
✍️ Note:
- You must ensure Pandas is installed using pip install pandas before importing.
- This method can be used to create simple school reports, attendance sheets, etc.
There are no comments for now.
